High cortisol levels can significantly impact your health. Cortisol is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands, crucial for various bodily functions. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and management of high cortisol levels.
Cortisol is often referred to as the “stress hormone.” It plays a vital role in the body’s stress response. When cortisol levels are consistently high, it can lead to serious health issues.
In this article, we will delve into the significance of high cortisol levels. We will discuss its effects on the body, potential causes, and effective management strategies. Understanding cortisol is essential for maintaining overall health.
The Role of Cortisol in the Body
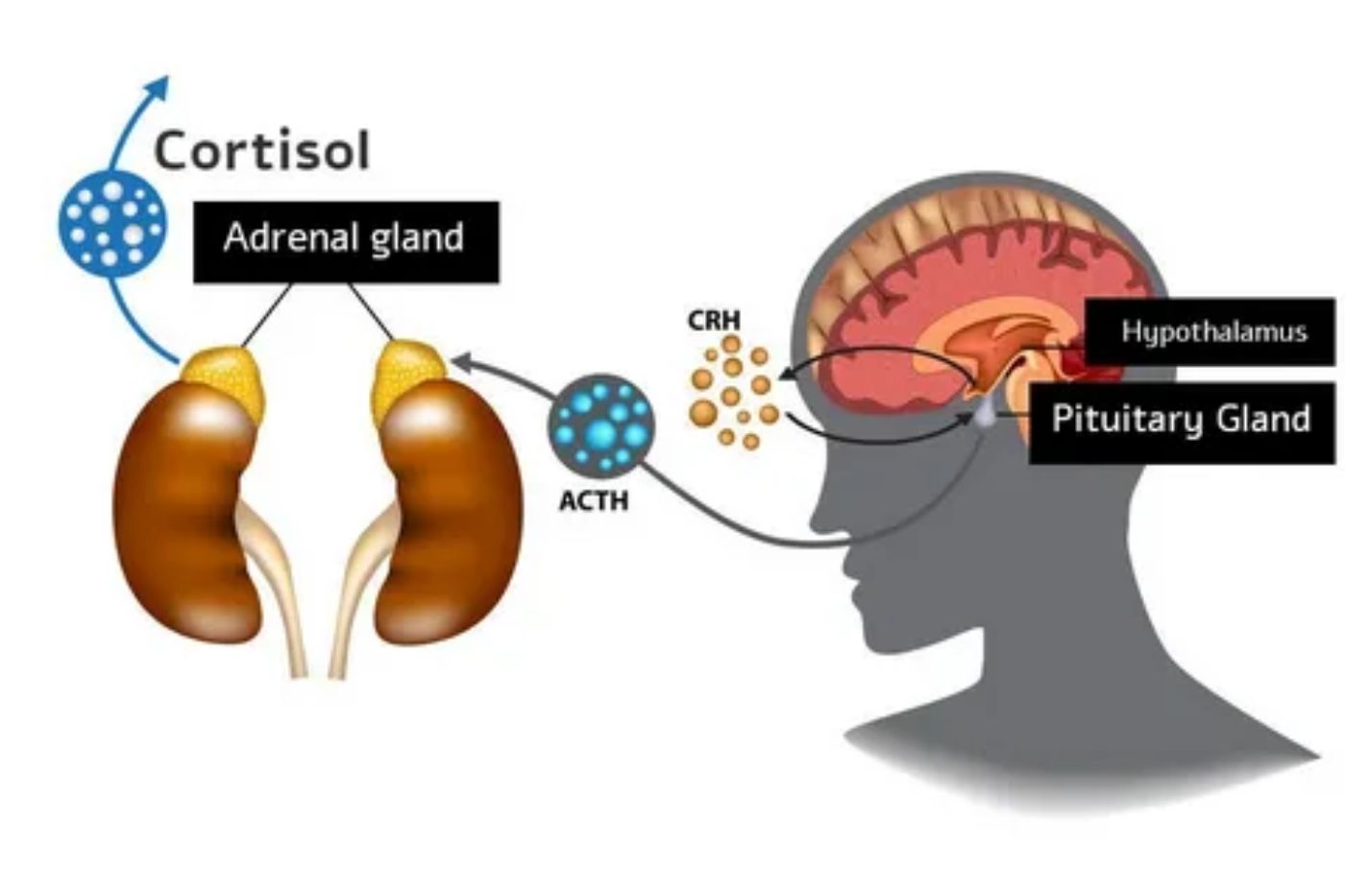
Cortisol is a glucocorticoid hormone produced by the adrenal glands. It helps regulate metabolism, blood pressure, and the body’s stress response. When faced with stress, the hypothalamus signals the pituitary gland to release adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which stimulates cortisol production.
Cortisol affects various systems in the body. It helps control blood sugar levels, reduces inflammation, and affects the sleep-wake cycle. However, when cortisol levels are high for prolonged periods, it can lead to adverse health effects.
Chronic high cortisol levels can disrupt hormonal regulation. This disruption may lead to conditions like Cushing’s syndrome or adrenal insufficiency. Understanding these effects is crucial for maintaining hormonal balance.
Best Way to Know Causes of High Cortisol Levels

High cortisol levels can arise from multiple sources. Chronic stress is one of the primary contributors. It can stem from work pressures, relationship issues, or financial problems. When stress becomes a constant factor, cortisol production increases.
Other factors contributing to high cortisol levels include poor diet, lack of sleep, and certain medical conditions. Conditions like Cushing’s syndrome lead to excessive cortisol production. Furthermore, medications such as corticosteroids can also elevate cortisol levels.
Understanding the causes of high cortisol is essential for effective management. Identifying stressors and addressing them can significantly reduce cortisol levels.
Symptoms of High Cortisol Levels
Recognizing the symptoms of high cortisol levels is crucial for timely intervention. Common symptoms include weight gain, especially around the abdomen and face. This is often due to changes in metabolism caused by high cortisol.
Other symptoms include fatigue, muscle weakness, and mood changes. Individuals may experience anxiety, depression, or irritability. Additionally, high cortisol can disrupt sleep patterns, leading to insomnia or sleep apnea.
Long-term effects of high cortisol levels can include high blood pressure and increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Understanding these symptoms helps in recognizing the need for medical evaluation.
Impact of High Cortisol Levels on Health
High cortisol levels can lead to severe health consequences. One significant impact is on the cardiovascular system. Prolonged high cortisol can raise blood pressure, increasing the risk of heart disease.
Moreover, high cortisol affects the immune system. It can suppress immune responses, making individuals more susceptible to infections. Chronic inflammation may also occur, which is linked to various diseases.
Additionally, high cortisol can disrupt metabolic processes. This disruption can lead to insulin resistance and high blood sugar levels. Understanding these health impacts highlights the importance of managing cortisol levels effectively.
How to Measure Cortisol Levels
Measuring cortisol levels can help diagnose high cortisol conditions. Various methods exist, including blood tests, urine tests, and saliva tests. Each method has its advantages and specific uses.
Blood tests measure cortisol levels at specific times. This can help assess daily fluctuations in cortisol production. Urine tests measure cortisol over 24 hours, providing a comprehensive view of cortisol levels.
Saliva tests are often used for assessing cortisol levels in a non-invasive way. They can be done at home and are especially useful for measuring cortisol levels during the night when they should be lower.
Management Strategies for High Cortisol Levels
Managing high cortisol levels involves addressing the underlying causes. Stress management techniques are essential. Practices such as mindfulness, yoga, and meditation can help reduce stress and cortisol levels.
Additionally, maintaining a balanced diet is crucial. Foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamins can support adrenal health. Reducing caffeine and sugar intake can also help regulate cortisol levels.
Regular exercise is another effective strategy. Physical activity helps lower cortisol levels and improve overall well-being. However, it is essential to avoid overtraining, which can have the opposite effect.
Lifestyle Changes to Lower Cortisol

Making specific lifestyle changes can significantly lower cortisol levels. Prioritizing sleep is vital. Aim for at least 7-9 hours of quality sleep each night to help regulate cortisol production.
Incorporating relaxation techniques into daily routines can also be beneficial. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and spending time in nature can help lower stress levels.
Establishing a social support system is essential. Connecting with friends and family can reduce feelings of isolation and stress, aiding in cortisol regulation.
The Connection Between Diet and Cortisol Levels
Diet plays a crucial role in managing cortisol levels. Certain foods can either help lower or raise cortisol. Incorporating whole foods, such as fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins, supports overall health.
Avoiding processed foods, high sugar, and caffeine can help stabilize cortisol. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish, walnuts, and flaxseeds, are particularly beneficial for adrenal health.
Staying hydrated is also essential. Dehydration can lead to increased cortisol production. Aim to drink enough water throughout the day to maintain hydration.
Understanding Cushing’s Syndrome
Cushing’s syndrome is a condition characterized by high cortisol levels. It can result from tumors on the adrenal glands or pituitary gland. Symptoms include rapid weight gain, skin changes, and muscle weakness.
Diagnosis involves measuring cortisol levels through various tests. Treatment often requires addressing the underlying cause, which may include surgery, radiation, or medication.
Understanding Cushing’s syndrome is vital for recognizing when to seek medical help. Early diagnosis can lead to better management and improved outcomes.
The Role of Adrenal Glands in Cortisol Production
The adrenal glands are small glands located on top of each kidney. They play a crucial role in hormone production, including cortisol. The adrenal cortex is responsible for producing cortisol in response to stress and other stimuli.
Dysfunction in the adrenal glands can lead to either high or low cortisol levels. Conditions such as adrenal insufficiency can result in low cortisol, while tumors can cause excessive cortisol production.
Monitoring adrenal health is essential for maintaining balanced cortisol levels. Regular check-ups with healthcare providers can help detect any issues early.
Read this Blog: 10 Ways to Control High Blood Pressure Without Medication
Effects of Chronic Stress on Cortisol Levels
Chronic stress is a significant factor contributing to high cortisol levels. When the body is under constant stress, it continuously produces cortisol. This continuous production can lead to various health issues.
Chronic high cortisol levels can disrupt the body’s normal functions. It can affect metabolism, immune responses, and even mood regulation. Understanding this connection highlights the importance of stress management.
Implementing stress-reduction techniques is crucial for mitigating the effects of chronic stress. Seeking counseling, practicing relaxation techniques, and engaging in hobbies can help lower stress levels.
The Importance of Regular Exercise

Regular exercise is a powerful tool for managing cortisol levels. Physical activity helps reduce stress and promotes the release of endorphins, improving mood. It can also enhance sleep quality, further supporting hormonal balance.
Different types of exercise can be beneficial. Aerobic exercises, such as running or swimming, effectively reduce cortisol levels. Strength training also contributes to overall health and well-being.
However, it’s essential to find a balance. Over-exercising can lead to increased cortisol levels, counteracting the benefits. Listening to your body and allowing time for recovery is crucial.
Comparison of Cortisol Level Measurement Methods
| Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Blood Test | Accurate, measures time-specific | Invasive, requires appointment |
| Urine Test | Comprehensive view over 24 hours | Collection can be cumbersome |
| Saliva Test | Non-invasive, easy to do at home | Less accurate than blood tests |
Final Insights
High cortisol levels can have profound effects on your health. Understanding the role of cortisol, its causes, and symptoms is essential for effective management. Elevated cortisol can lead to serious health issues, including cardiovascular diseases and metabolic disorders.
Lifestyle changes, such as stress management techniques, balanced nutrition, and regular exercise, can significantly help in regulating cortisol levels. It is crucial to prioritize sleep and incorporate relaxation practices into daily life to support hormonal balance.
By taking proactive steps and seeking medical advice when necessary, you can effectively manage high cortisol levels. This approach not only improves your health but also enhances your overall quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main causes of high cortisol levels?
Chronic stress, poor diet, lack of sleep, and certain medical conditions can all contribute.
How can I naturally lower my cortisol levels?
Practicing stress management techniques, exercising regularly, and maintaining a healthy diet can help.
What are the symptoms of high cortisol levels?
Common symptoms include weight gain, fatigue, anxiety, and disrupted sleep patterns.
How is high cortisol diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves blood, urine, or saliva tests to measure cortisol levels.
Can high cortisol levels lead to serious health issues?
Yes, prolonged high cortisol levels can increase the risk of cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and other health problems.
What lifestyle changes can help manage cortisol levels?
Prioritizing sleep, practicing relaxation techniques, and maintaining a balanced diet are essential

Zade Smith is a Proficient writer on TechsBlip, dedicated to delivering high-quality content that bridges the gap between medical research and accessible, reader-friendly guidance. With a keen interest in promoting healthy lifestyles and disease prevention, Zade’s writing offers expert insights, actionable tips, and evidence-based information to help readers make informed decisions about their health and wellness